What Happens to a Catalyst in a Reaction Apex
How does a catalyst impact a reaction. Catalysts lower the activation energy the energy required for a reaction to occur so that a reaction can happen.
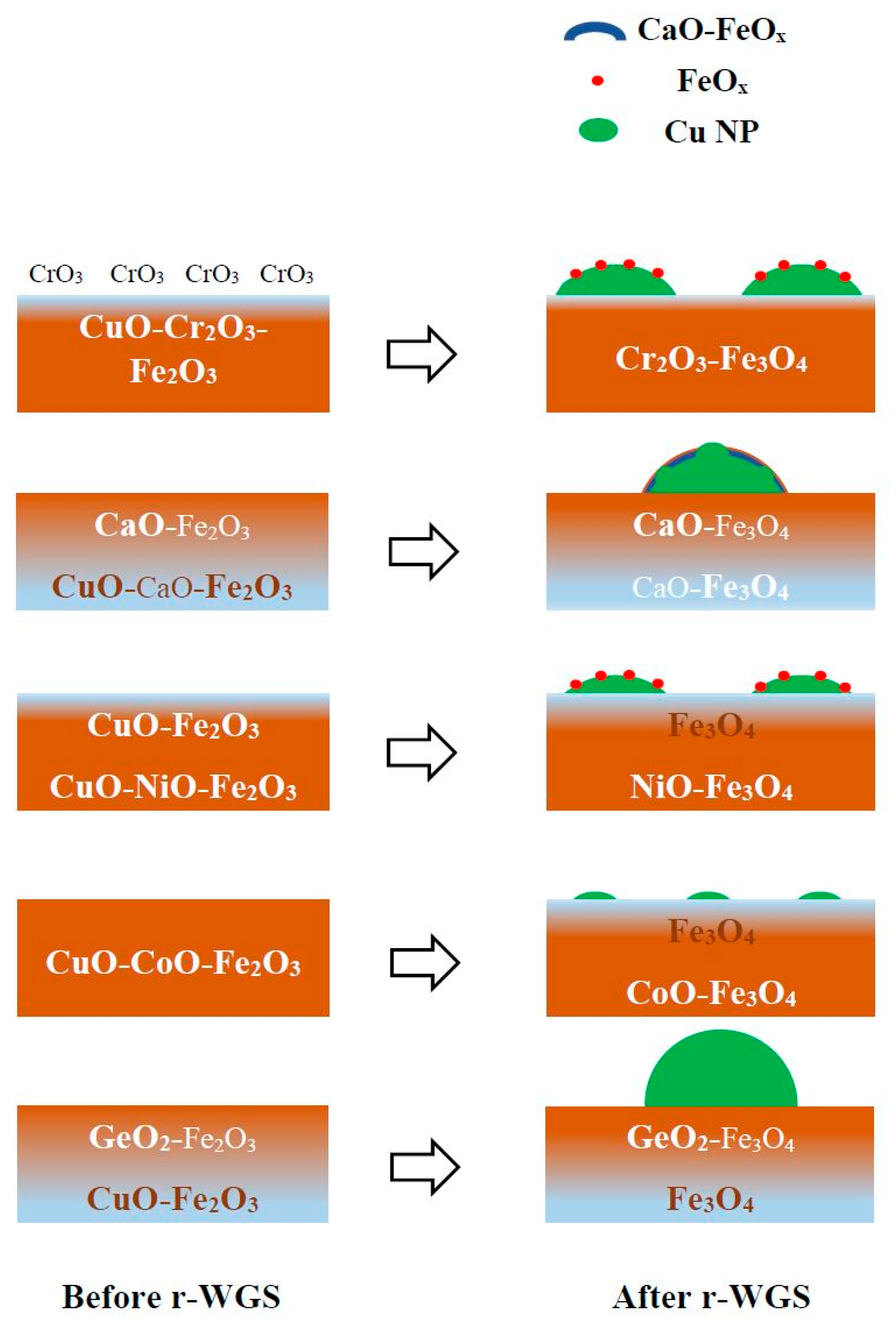
Catalysts Free Full Text Cr Free Cu Promoted Fe Oxide Based Catalysts For High Temperature Water Gas Shift Ht Wgs Reaction Html
Essentially the action of the catalyst is to provide an alternative lower energy pathway for the reaction.
. So catalysts do undergo chemical changes in the catalytic reaction but are regenerated after the catalytic reaction is finished. By lowering the activation energy the rate constant is greatly increased. You can view this as the catalyst speeding up the forward and reverse reactions.
For example ethanol is metabolized into acetaldehyde by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase. Which statement is true of a catalyst in a reaction. Chemistry 22062019 1030 Brookwiggington8814.
This means that if you are using a catalyst you can normally reuse it after your catalytic reaction because it has the same chemical and physical properties as before the catalytic reaction. Catalysts and activation energy. Catalyzed reactions are typically used to accelerate the rate by which a specific chemistry proceeds.
After the reaction occurs a catalyst returns to its original state and so catalysts can be used over and over again. Catalysts speed up a chemical reaction by lowering the. Typically increased concentrations of reactants increases the speed of the reaction because there are more molecules colliding and.
It increases the reaction rate by lowering the activation energy for a reaction. Catalyst A chemical substance that alters either increases or decreases the rate of a chemical reaction is known as a catalyst. This intermediate is temporary in that after it forms it breaks apart and leaves the original catalyst species unchanged.
Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0 Add a Comment. The rate law uses the molar concentrations of reactants to determine the reaction rate. Generally the role of the catalyst is to provide an alternative low energy pathway for a reaction.
Catalysts are used to speed. Catalysts speed up chemical reactions. It makes a reaction faster by adding energy.
How does concentration affect the rate of a reaction. Once they do it bows out. What does the rate law used to determine the rate of a reaction.
For example a catalyst could cause a reaction between reactants to happen at a faster rate or at a lower temperature than would be possible without the catalyst. To increase the rate of a reaction you need to increase the number of successful collisions. Effect of Catalyst on Activation Energy.
Click to see full answer. It acts as a reactant in place of the original reactant. It gets used up in the reaction.
A catalyst increases the rate of the reaction by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction that has a lower activation energy. 3 Get Other questions on the subject. In the absence of ADH the rate of the reaction would be less than 0000006 or 6 x 10-6 µmolesL per minute.
This happens by altering the activation energy of a reaction. What can be done to speed up a reaction. Like a wingman it encourages other molecules to react.
One possible way of doing this is to provide an alternative way for the reaction to happen which has a lower activation energy. What kind of reaction occurs when the entropy change of an endothermic. The speed at which a reaction occurs apex This answer is.
What happens when a catalyst is used in a chemical reaction. A reaction can also be sped up by adding a catalyst to the reaction mixture. For this to occur the catalytic substance interacts with a reactant and forms an intermediate compound.
A catalyst can act in two ways It can either be a promoter or poison for the reactiona positive catalyst increases the rate of reaction by decreasing the activation energy of the reaction means reaction becomes faster whereas a negative catalyst decreases the reaction rate or it can completely arrest the reaction. In this synthesis reaction what products will form. Chemistry 21062019 1940 raquelqueengucci25.
What happens when catalyst is used. Catalysts accelerate reactions by reducing the energy of the rate-limiting transition state. The reaction will shift to the right toward the products.
Manufacturers often create catalysts to speed processes in industry. Which would speed up a reaction. In other words to move the activation energy on the graph like this.
Simply so what happens to catalysts during a reaction. A catalyst lowers the barrier for the activation energy. The reaction rate increases.
A catalyst lowers activation energy and increases the rate of a chemical reaction to a great extent. The reaction rate decreases. There will be no effect.
For this to happen the catalyst interacts with a reactant and forms an intermediate compound. An alternate reaction pathway with a lower activation energy an alternate reaction pathway with a higher activation energy the same reaction pathway with a lower activation energy the same reaction pathway with a higher activation energy Answer and Explanation. Catalysts are compounds that accelerate the rate of a reaction.
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy without being used up in the reaction. A chemical catalyst is a substance that causes a chemical reaction to happen in a different way than it would happen without that catalyst. What happens to a catalyst in a reaction.
The reaction will shift to the left toward the reactants. What occurs when a catalyst is added to a chemical reaction. What woukd most likely be the transmittance at a 070 m solution of.
Enzymes are biologys natural catalysts. While in the presence of ADH the reaction rate is 2700 µmolesL per minute. The reaction process decreases.
In essence a catalyst will cause a reaction to reach equilibrium faster. They play a role in everything from copying genetic material to breaking down food and nutrients. Catalysts do not alter a chemical reaction in terms of the product.
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction but is not consumed during the course of the reaction. The reaction will stay at equilibrium. It changes the activation energy required for the reaction.
The reaction rate does not change. In addition to dimerization reactions two other examples are the decomposition of NO2 to NO and O2 and the decomposition of HI to I2 and H2. A catalyst doesnt get used up in the reaction though.

What Happens To A Catalyst In A Reaction Brainly Com
Solved Which Statement Best Explains The Role Of A Catalyst Chegg Com

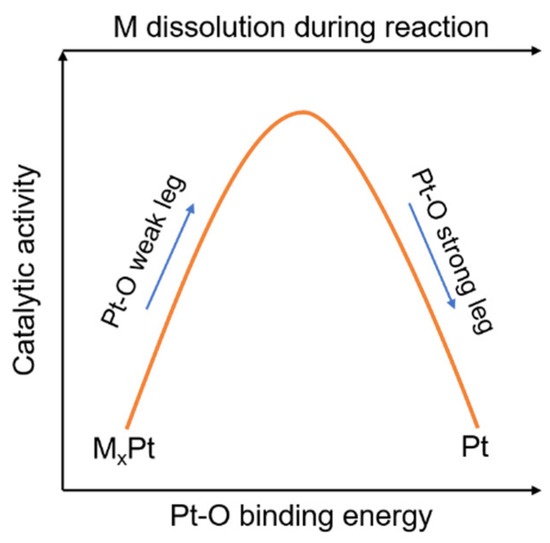
Catalysts Free Full Text Low Pt Alloyed Nanostructures For Fuel Cells Catalysts Html
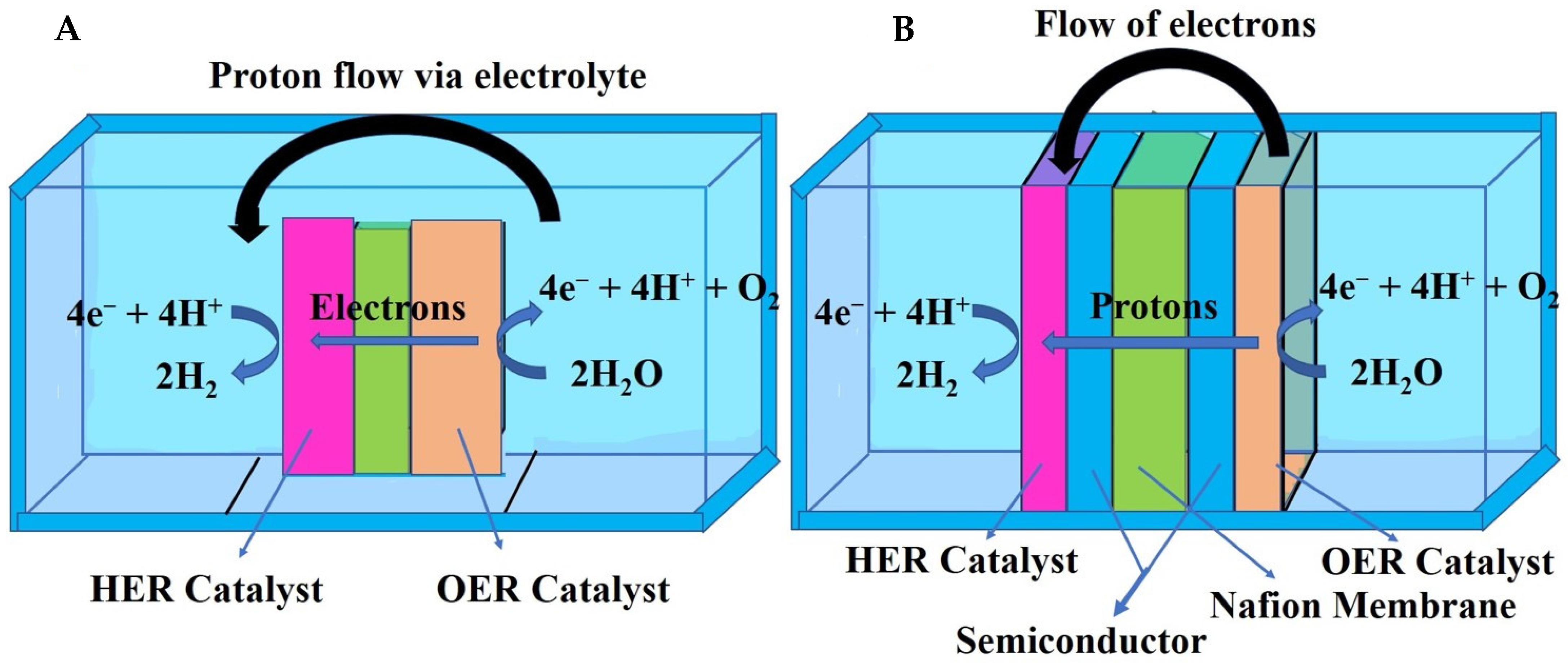
Catalysts Free Full Text Earth Abundant Electrocatalysts For Water Splitting Current And Future Directions Html
Catalysts Free Full Text Cr Free Cu Promoted Fe Oxide Based Catalysts For High Temperature Water Gas Shift Ht Wgs Reaction Html

What Happens To A Catalyst Used In A Reaction O A It Is Unchanged By The Reaction Ob It Is Bonded Brainly Com

Characterization Of Catalysts By Advanced Scanning Probe Microscopy And Spectroscopy Sun 2020 Chemcatchem Wiley Online Library

No comments for "What Happens to a Catalyst in a Reaction Apex"
Post a Comment